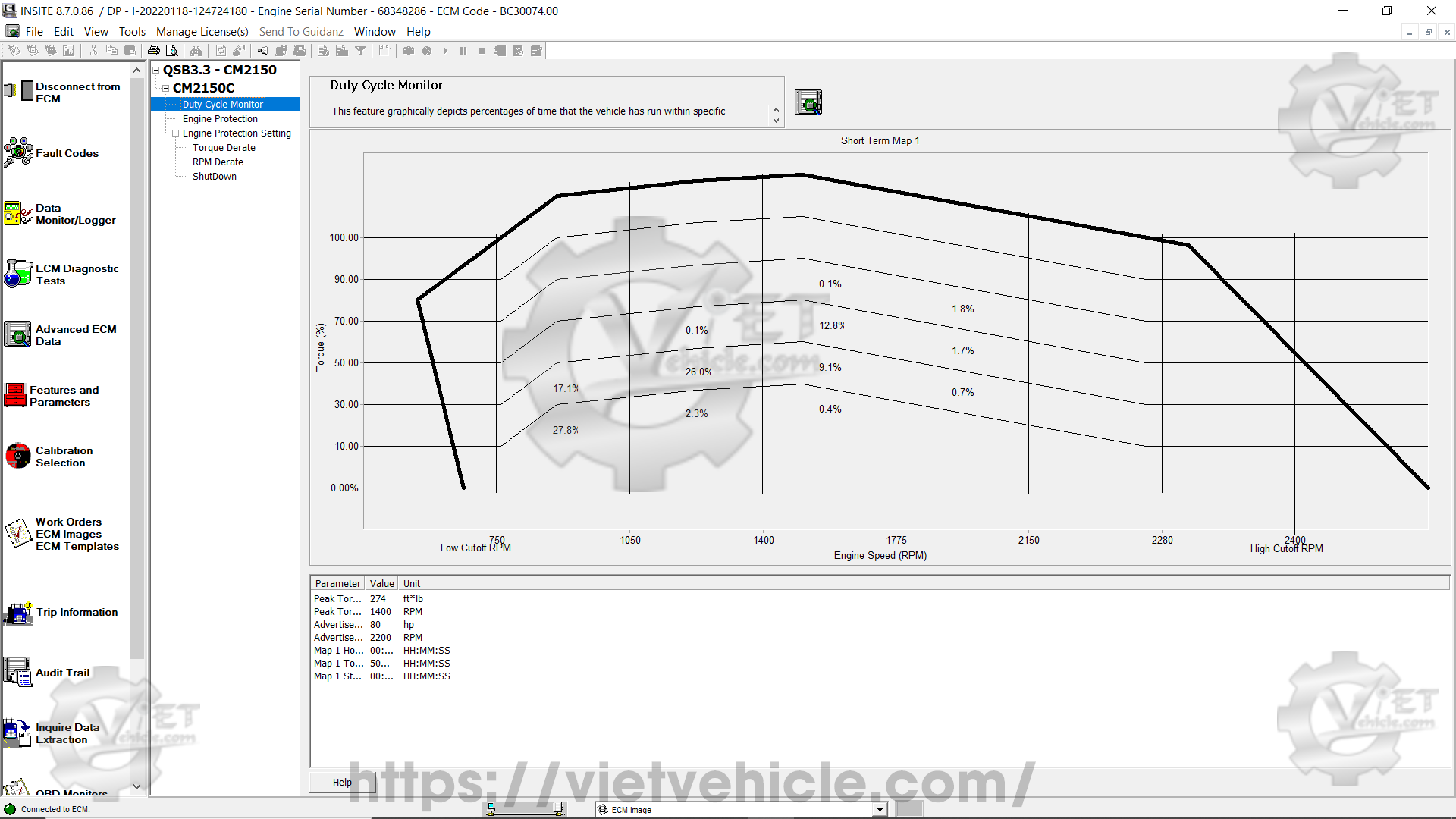
Figure 1.1 – Duty Cycle Monitor (Short Term Map 1)
To access the Advanced ECM Data:
1). Attach the diagnostic adapter tool (Nexiq USB-Link) to the diagnostic port of the Cummins Engine or ECM Image. Refer to: How to Connect CUMMINS Engines using Cummins INSITE Software.
2). Select Advanced ECM Data from the Viewbar, as Figure 1.2 below.
Figure 1.2 – Advanced ECM Data
(A) Duty Cycle Monitor
The Duty Cycle Monitor visually represents the percentage of time the vehicle has operated within specific performance ranges.
These operational ranges are determined by engine speed (rpm) compared to torque.
The X-axis of the graph represents engine speed, while the Y-axis represents torque.
The rpm and torque values are specified by the engine calibration.
A bold line appears on the graph to serve as a general reference for the torque curve.
This torque curve reference remains the same for all engine models.
Each section of the graph represents a combination of rpm and torque values defining a particular operating range.
The percentage displayed in each section represents the portion of total operation time spent in that specific range.
For instance, if the graph represents a total of 500 operating hours and a section shows 5%, the vehicle has spent 25 hours in that range.
The total percentage values displayed on the graph may slightly exceed or fall short of 100% due to rounding when INSITE™ retrieves data from the ECM.
Three different Duty Cycle maps are available in the Duty Cycle Monitor window:
a). Short Term Map 1 (as shown in Figure 1.1 above).
This map records up to 500 hours of data. Once the 500-hour limit is reached, INSITE automatically starts logging onto Short Term Map 2.
b). Short Term Map 2.
This map also logs 500 hours of operational data. INSITE automatically transitions to this map after Short Term Map 1 reaches its limit.
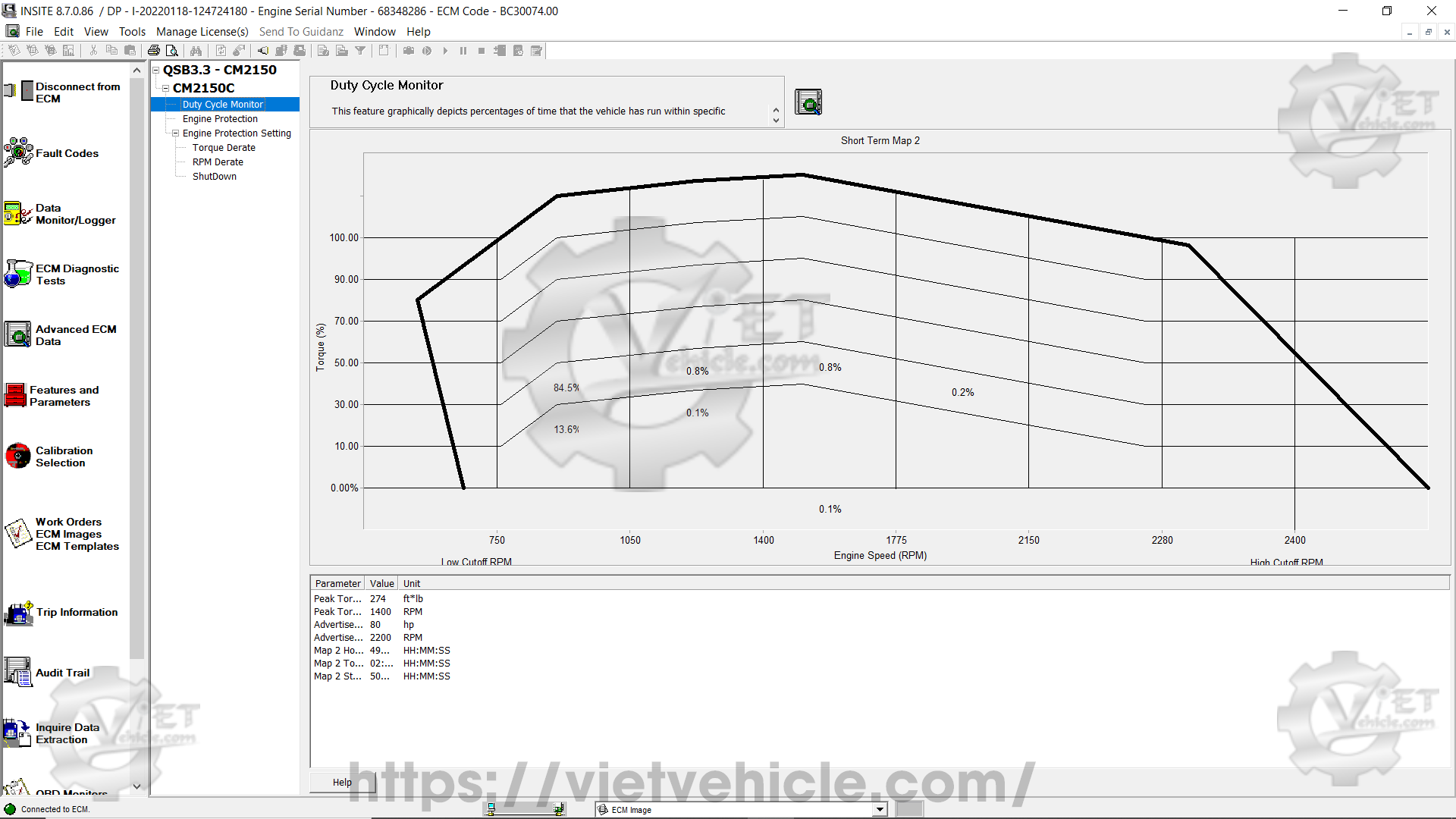
Figure 1.3 – Duty Cycle Monitor (Short Term Map 2)
c). Long Term Map.
This map captures engine operating ranges throughout the entire lifespan of the engine or vehicle.
Unlike short-term maps, this map cannot be reset.
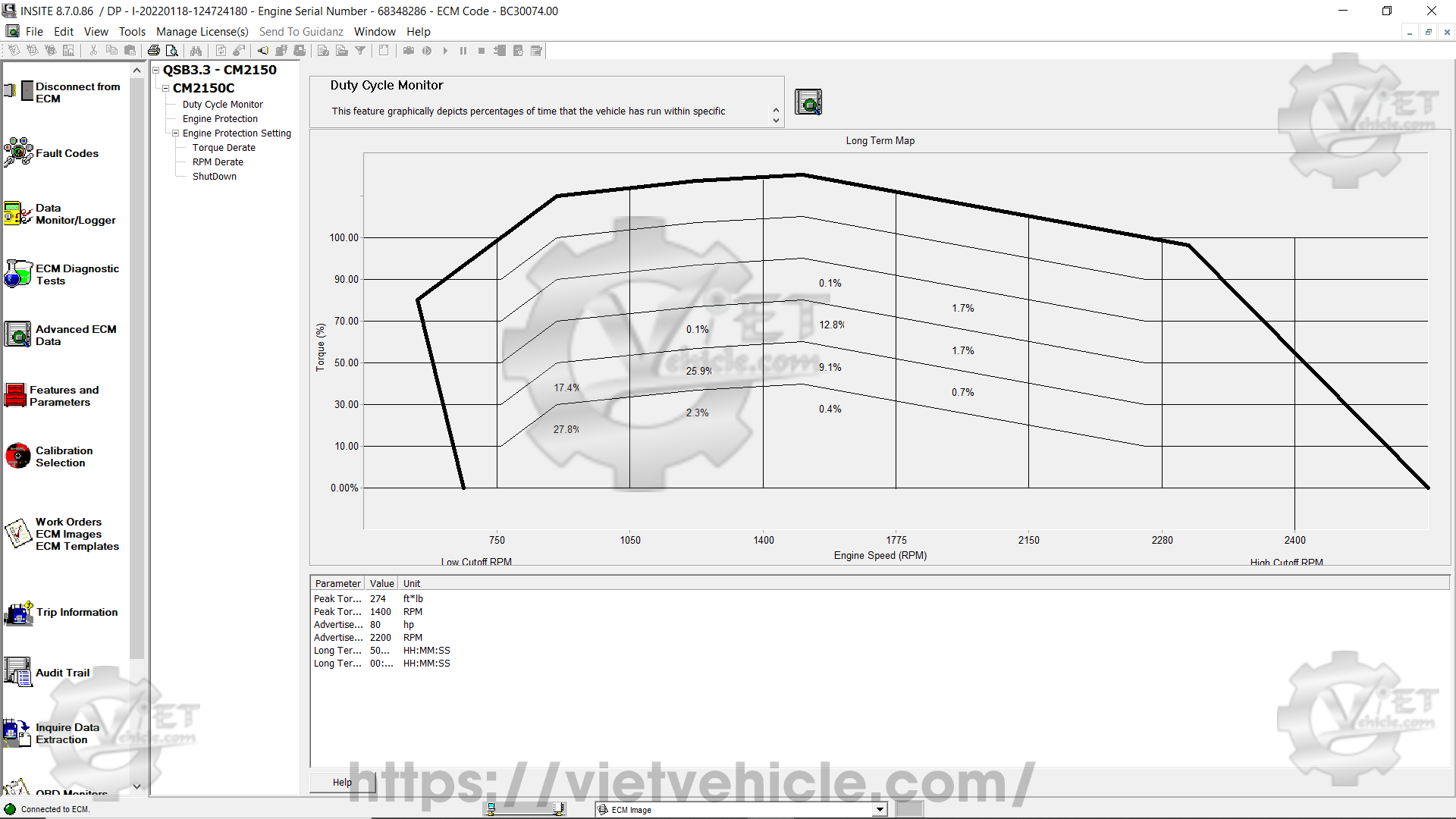
Figure 1.4 – Duty Cycle Monitor (Long Term Map)
Note:
Time Remaining – Displays the remaining duration of the selected map. The Short Term Maps last for 500 hours, whereas the Long Term Map has an indefinite duration.
Map Start Time – Indicates the ECM timestamp when data logging began for the active map.
Advertised Power RPM – Specifies the engine speed at which the peak power output is achieved.
Advertised Power at RPM – Represents the highest horsepower rating of the engine.
Replace Torque RPM – Displays the engine speed at which peak torque is generated.
Peak Torque at RPM – Refers to the maximum torque capability of the engine.
(B) Engine Protection Setting
The Engine Protection system is designed to safeguard the engine from damage when a sensor reading surpasses a predetermined threshold for critical operating parameters.
The Engine Protection feature allows users to review the fault history linked to a specific engine protection error.
A historical log is maintained for each Engine Protection parameter.
The last five instances of each Engine Protection fault are recorded and displayed.
Torque Derate / RPM Derate
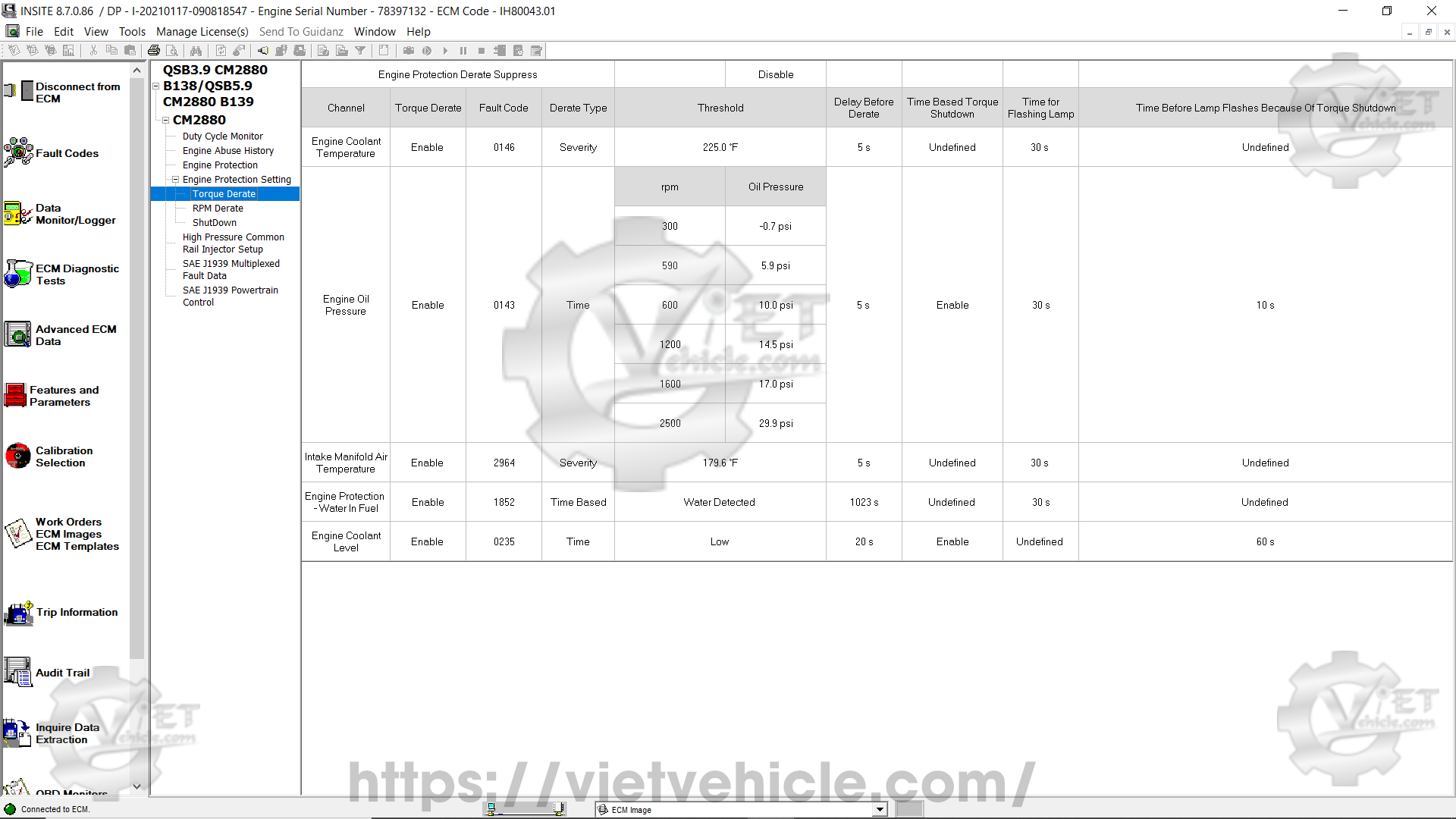
Figure 1.5 – Torque Derate
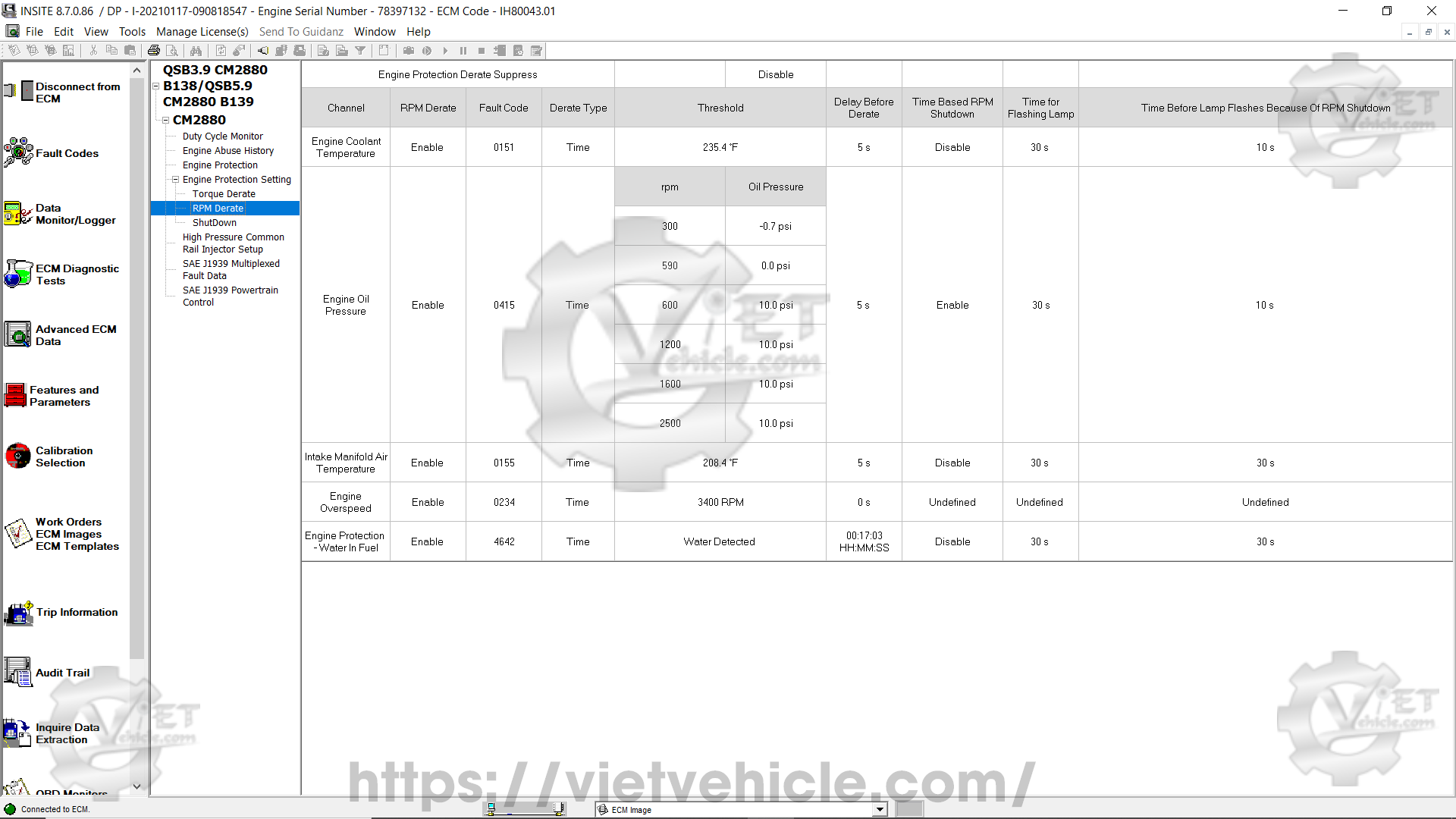
Figure 1.6 – RPM Derate
(C) Engine Protection
Figure 1.7 – Engine Protection
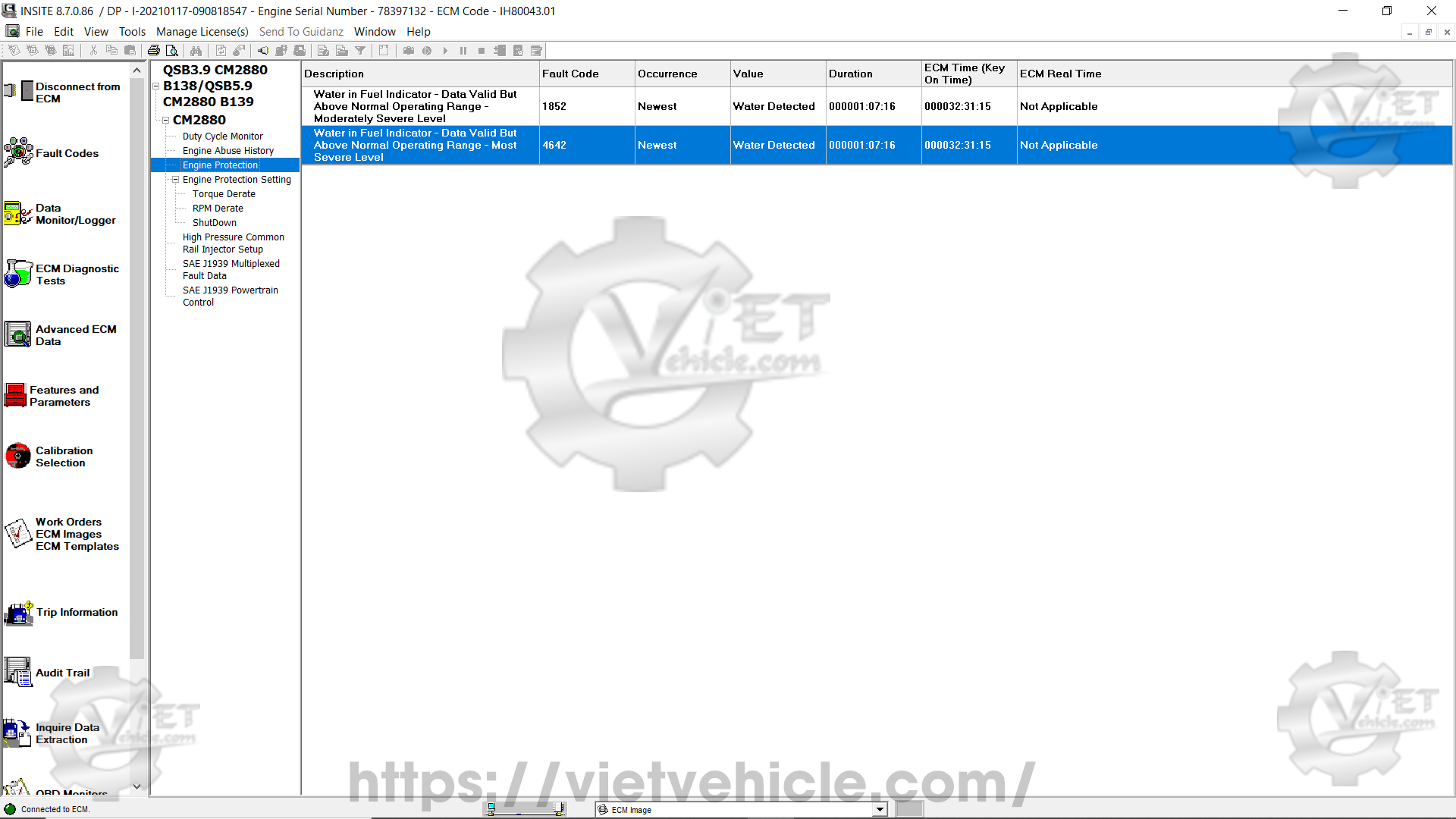
Figure 1.8 – Shutdown
(D) Engine Abuse History
The Engine Abuse History function logs instances where the engine has operated beyond recommended performance limits.
This feature provides detailed insights into the engine’s lifespan, usage patterns, maintenance history, and any excessive strain it may have undergone.
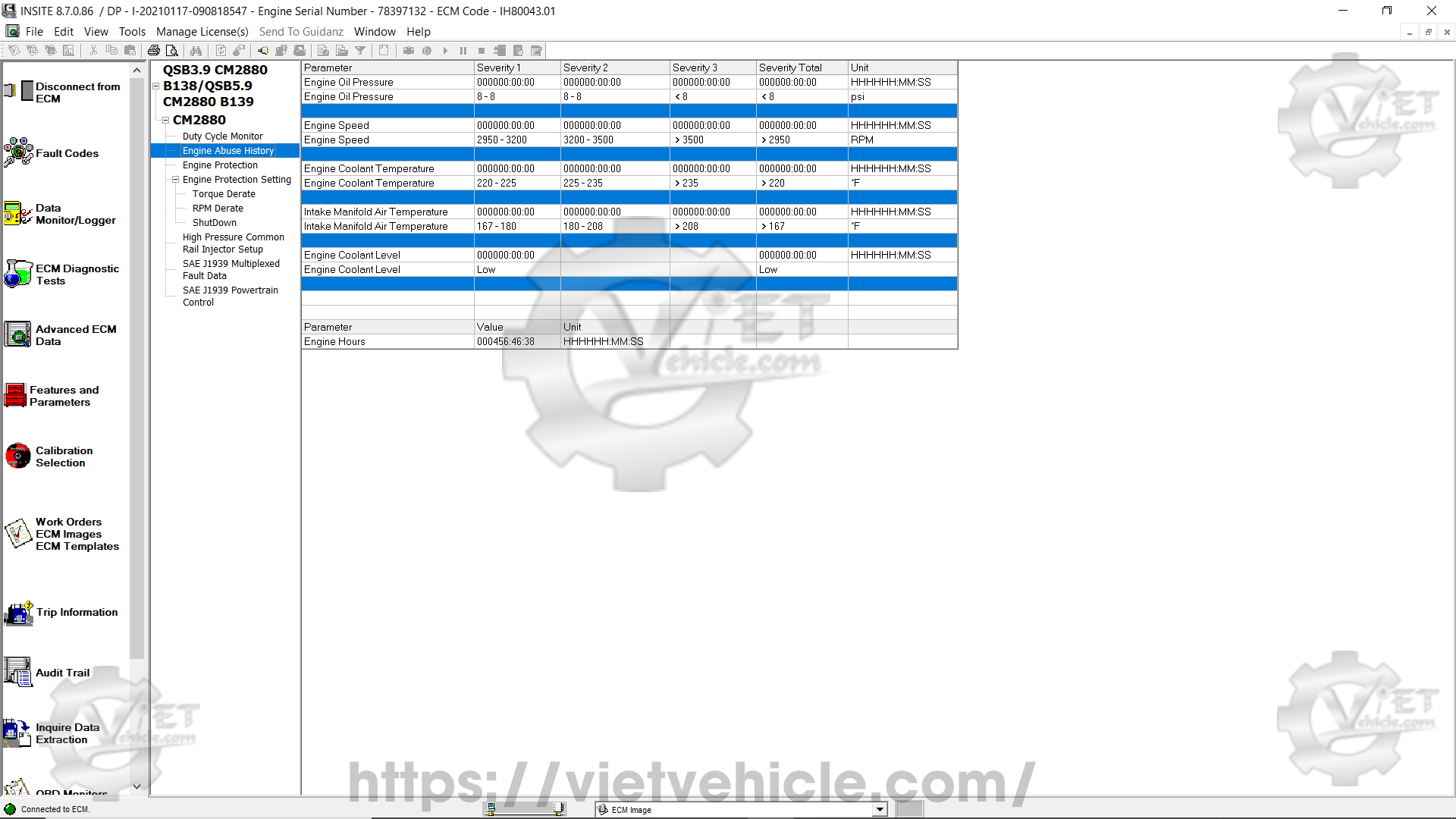
Figure 1.9 – Engine Abuse History
(E) High-Pressure Common Rail Injector Setup
This specialized feature allows users to display and update the barcode values assigned to each injector installed in the engine.
The Injector Barcode is an alphanumeric sequence that is physically engraved on the injector.
This barcode is used to characterize the fueling properties of the injector.
The ECM utilizes this barcode data to refine injection commands, ensuring accurate fueling and reducing injector-to-injector inconsistencies.
It is essential to update this barcode information when replacing an injector or ECM.
The manual input method should be used when an injector is replaced.
The import procedure is required when replacing or performing a ROM boot on an ECM.
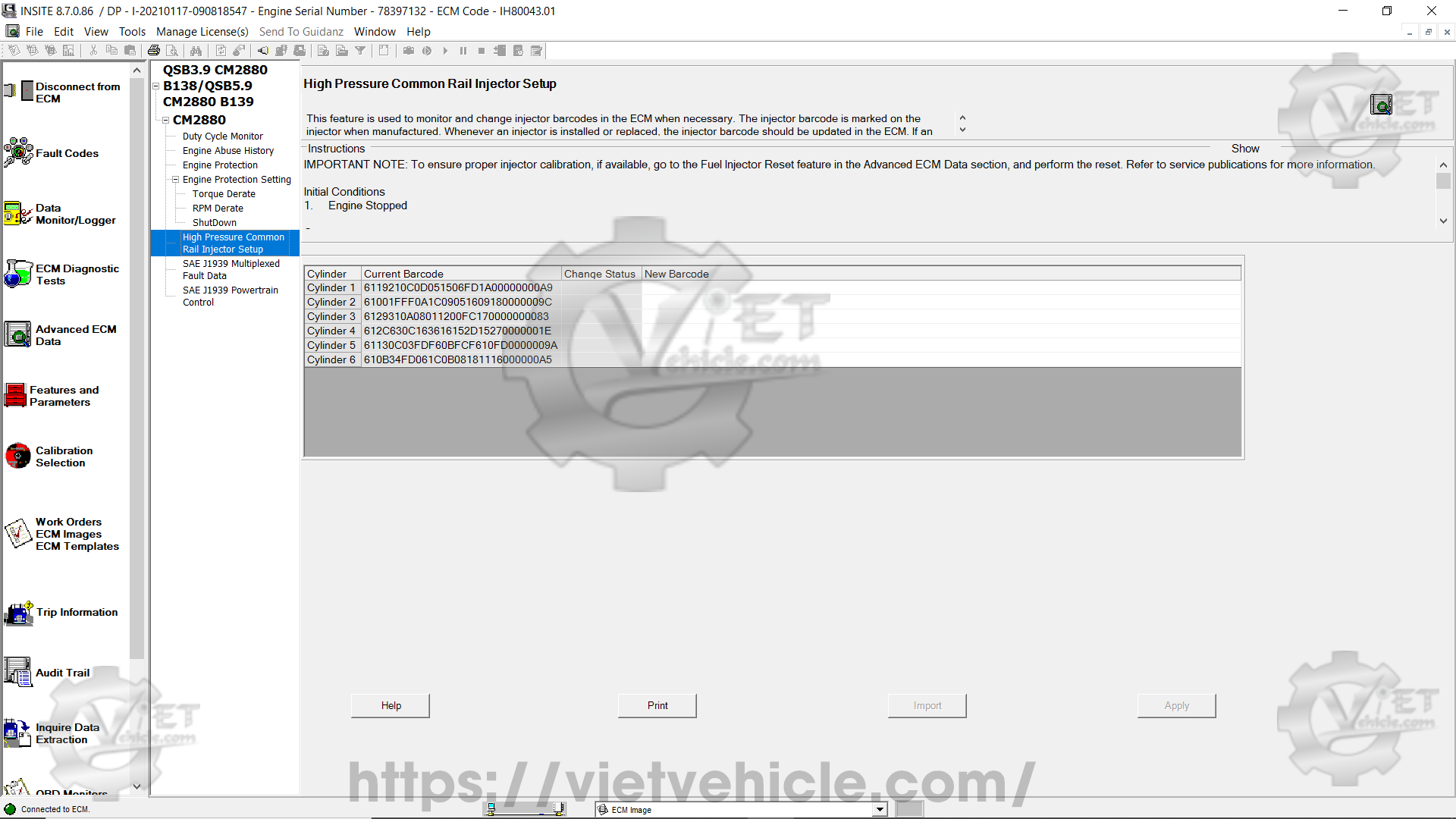
Figure 2.1 – High-Pressure Common Rail Injector Setup
(F) SAE J1939 Multiplexed Fault Data
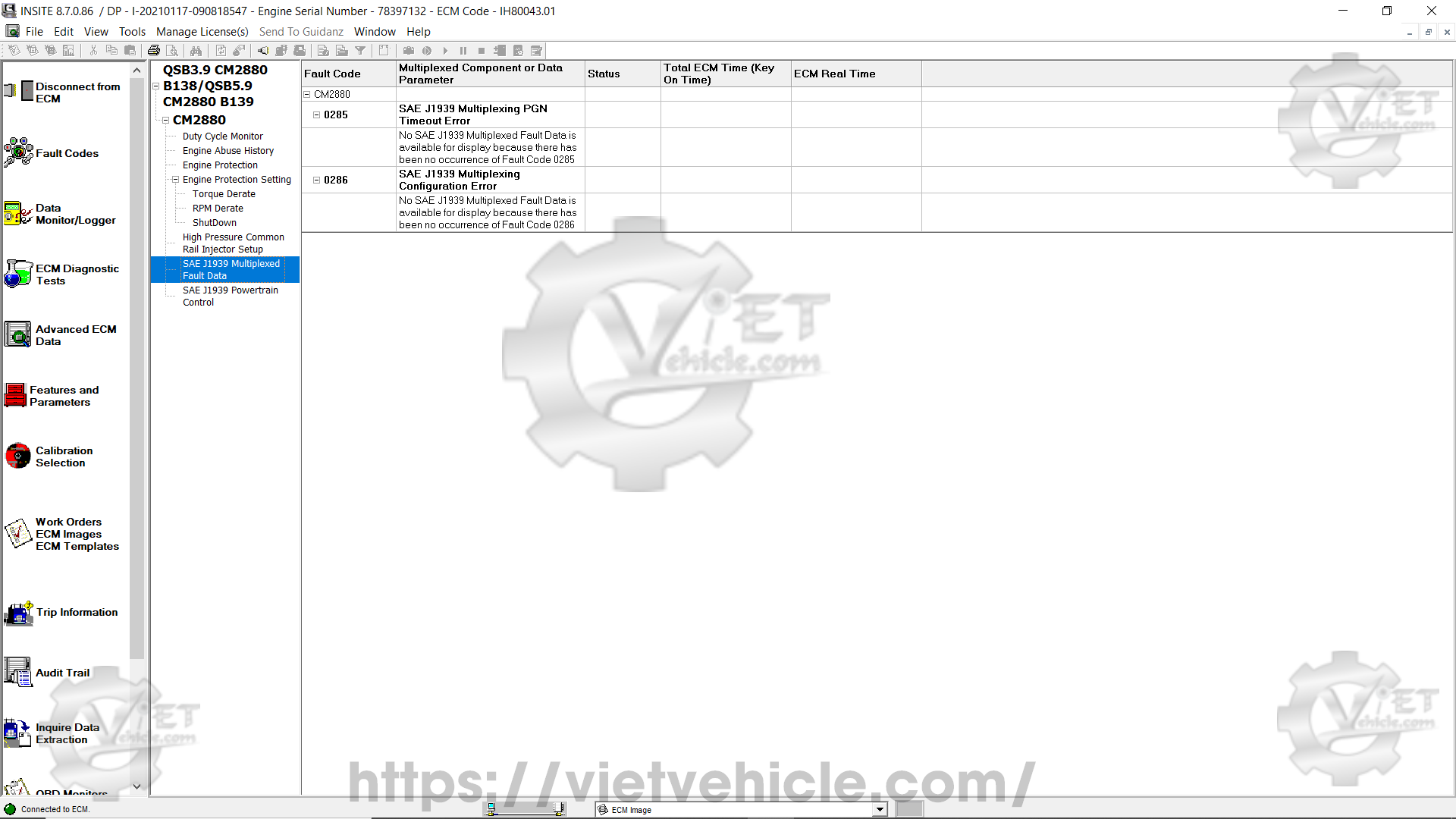
Figure 2.2 – SAE J1939 Multiplexed Fault Data
(G) SAE J1939 Powertrain Control
The SAE J1939 Powertrain Control function allows onboard vehicle control systems, such as Acceleration Slip Regulation (ASR) for traction control or electronically managed transmissions, to take command of the engine and its subsystems via the SAE J1939 datalink (network).
This feature enables users to review a historical record of instances when the engine was managed by a J1939 control device.
Maintaining a record of ECM control attempts through a J1939 device can be valuable for troubleshooting purposes.
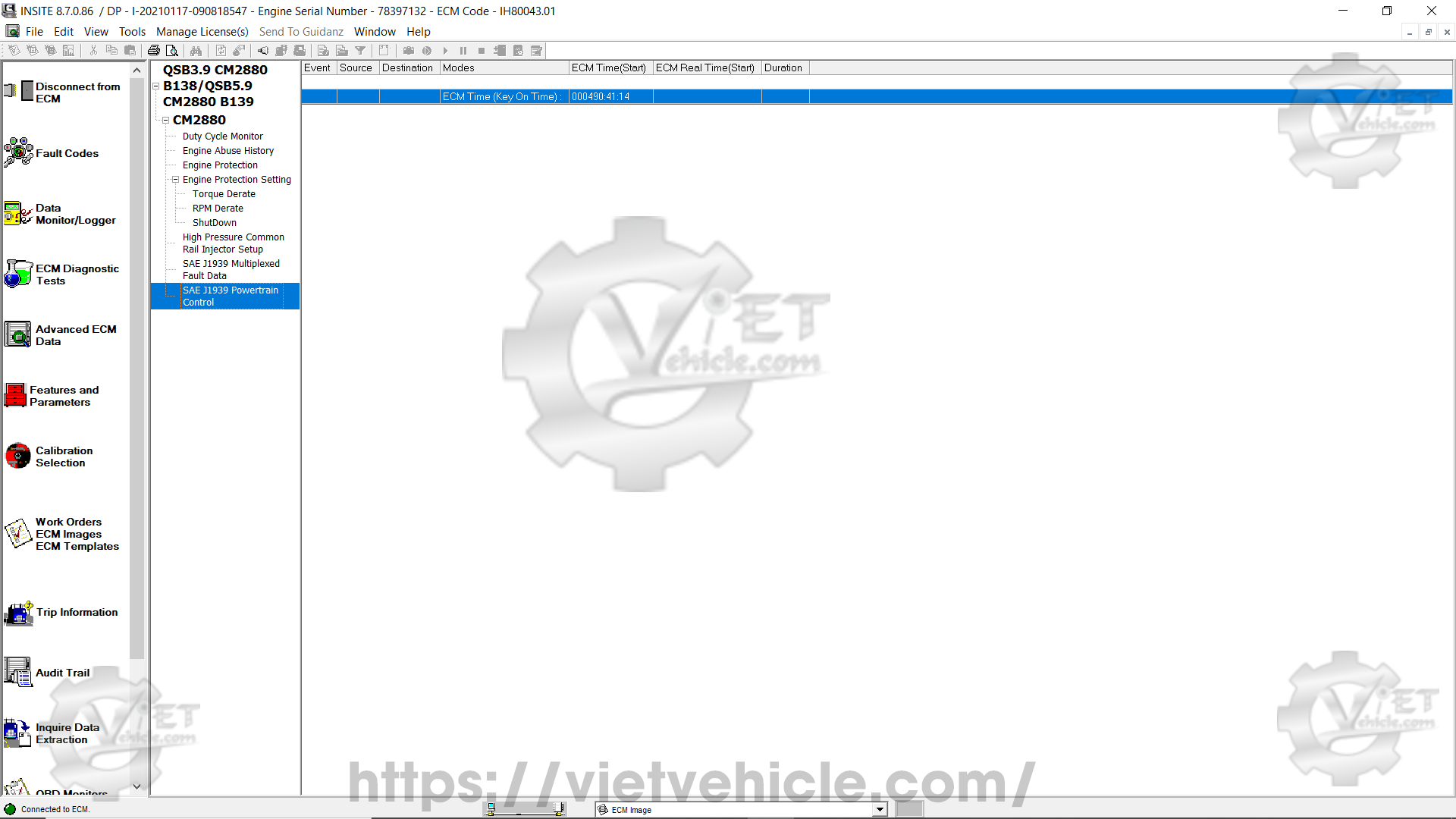
Figure 2.3 – SAE J1939 Powertrain Control
Contact Us
Whatsapp: +84.858.966.333
Facebook: VIETVehicle Remote Delete Service
YouTube: VIETVehicle – ECM Delete Tuning
Tiktok: VIETVehicle.com
Website: VIETVehicle.com